OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Trendlines Oscillator [LuxAlgo]
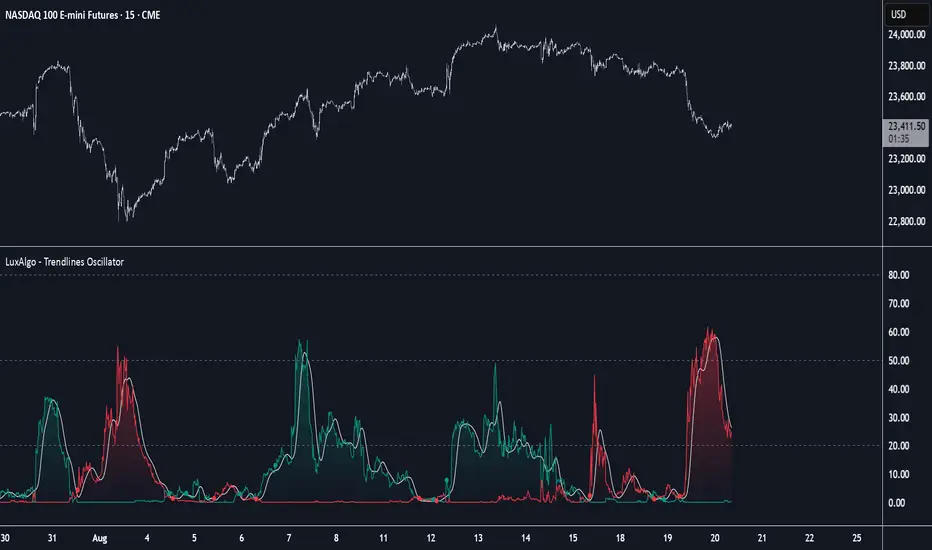
The Trendlines Oscillator helps traders identify trends and momentum based on the normalized distances between the current price and the most recently detected bullish and bearish trend lines.
The indicator features bullish and bearish momentum, a signal line with crossings, and multiple smoothing options.
🔶 USAGE

The indicator displays three lines: two for momentum and one for the signal. When one of the momentum lines (bullish or bearish) crosses the signal line, the tool displays a dot to indicate which momentum is gaining strength.
As a general rule, when the green bullish momentum line is above the red bearish momentum line, it indicates buyer strength. This means that the actual prices are farther from the support trend lines than the resistance trend lines. The opposite is true for seller strength.
To calculate bullish momentum, the tool first identifies bullish trend lines acting as support below the price. Then, it measures the delta between the price and those trend lines and normalizes the reading into the displayed momentum values.
The same process is used for bearish momentum, but with bearish trendlines acting as resistance above the price.
🔹 Length & Memory

Modifying the Length and Memory values will cause the tool to display different momentum values.
Traders can adjust the length to detect larger trendlines and adjust the memory to indicate how many trendlines the tool should consider.
As the chart above shows, smaller values make the tool more responsive, while larger values are useful for detecting larger trends.
🔹 Smoothing

By default, the data is not smoothed, and the signal uses a triangular moving average with a length of 10. Traders can smooth both the data and the signal line.
Traders can choose from up to ten different methods, or none. Some examples are shown on the chart above.
🔶 DETAILS
The steps for the calculations are as follows:
1. Gather the pivots, highs, and lows.
Pine Script®
2. Calculate the slope and y-intercept for each trendline between contiguous lower highs (resistance) or higher lows (support).
Pine Script®
3. Calculate the value of each trendline on the current bar, then calculate the difference with the current price (delta). To calculate the relative sum of deltas, only consider trendlines below the price for support or above the price for resistance.
Pine Script®
4. Normalize the value from 0 to 100 by taking the sum of the relative values of the deltas divided by the sum of the absolute values of the deltas.
Pine Script®
5. Smooth both values, then calculate the signal line as the difference between them.
Pine Script®
6. Calculate the crossing signals against the signal line, using only the first signal from each series of bullish or bearish crossings.
Pine Script®
🔶 SETTINGS
🔹 Smoothing
The indicator features bullish and bearish momentum, a signal line with crossings, and multiple smoothing options.
🔶 USAGE
The indicator displays three lines: two for momentum and one for the signal. When one of the momentum lines (bullish or bearish) crosses the signal line, the tool displays a dot to indicate which momentum is gaining strength.
As a general rule, when the green bullish momentum line is above the red bearish momentum line, it indicates buyer strength. This means that the actual prices are farther from the support trend lines than the resistance trend lines. The opposite is true for seller strength.
To calculate bullish momentum, the tool first identifies bullish trend lines acting as support below the price. Then, it measures the delta between the price and those trend lines and normalizes the reading into the displayed momentum values.
The same process is used for bearish momentum, but with bearish trendlines acting as resistance above the price.
🔹 Length & Memory
Modifying the Length and Memory values will cause the tool to display different momentum values.
Traders can adjust the length to detect larger trendlines and adjust the memory to indicate how many trendlines the tool should consider.
As the chart above shows, smaller values make the tool more responsive, while larger values are useful for detecting larger trends.
🔹 Smoothing
By default, the data is not smoothed, and the signal uses a triangular moving average with a length of 10. Traders can smooth both the data and the signal line.
Traders can choose from up to ten different methods, or none. Some examples are shown on the chart above.
🔶 DETAILS
The steps for the calculations are as follows:
1. Gather the pivots, highs, and lows.
ph = fixnan(ta.pivothigh(lengthInput, lengthInput))
pl = fixnan(ta.pivotlow(lengthInput, lengthInput))
2. Calculate the slope and y-intercept for each trendline between contiguous lower highs (resistance) or higher lows (support).
if ph < ph[1]
slope = (ph - ph[1])/(n-lengthInput - phx1)
res.unshift(l.new(ph[1] - slope * phx1, slope))
if pl > pl[1]
slope = (pl - pl[1])/(n-lengthInput - plx1)
sup.unshift(l.new(pl[1] - slope * plx1, slope))
3. Calculate the value of each trendline on the current bar, then calculate the difference with the current price (delta). To calculate the relative sum of deltas, only consider trendlines below the price for support or above the price for resistance.
method get_point(l id, x)=>
id.slope * x + id.intercept
for element in sup
point = element.get_point(n)
if sourceInput > point
sup_sum += sourceInput - point
sup_den += math.abs(sourceInput - point)
for element in res
point = element.get_point(n)
if sourceInput < point
res_sum += point - sourceInput
res_den += math.abs(point - sourceInput)
4. Normalize the value from 0 to 100 by taking the sum of the relative values of the deltas divided by the sum of the absolute values of the deltas.
float supportLine = sup_sum / sup_den * 100
float resistanceLine = res_sum / res_den * 100
5. Smooth both values, then calculate the signal line as the difference between them.
float smoothSupport = smooth(supportLine,dataSmoothingInput,dataSmoothingLengthInput)
float smoothResistance = smooth(resistanceLine,dataSmoothingInput,dataSmoothingLengthInput)
float signal = math.abs(smoothSupport - smoothResistance)
float signalLine = smooth(signal,smoothingInput,smoothingLengthInput)
6. Calculate the crossing signals against the signal line, using only the first signal from each series of bullish or bearish crossings.
bullSignal = smoothSupport > signalLine and smoothSupport[1] < signalLine[1]
bearSignal = smoothResistance > signalLine and smoothResistance[1] < signalLine[1]
lastSignal := bullSignal and lastSignal == BEAR ? BULL : bearSignal and lastSignal == BULL ? BEAR : lastSignal
firstBull = ta.change(lastSignal) > 0
firstBear = ta.change(lastSignal) < 0
🔶 SETTINGS
- Length: The size of the market structure used for trendline detection.
- Memory: The number of trendlines used in calculations.
- Source: The source for the calculations is closing prices by default.
🔹 Smoothing
- Data Smoothing: Choose the smoothing method and length
- Signal Smoothing: Choose the smoothing method and length
Açık kaynak kodlu komut dosyası
Gerçek TradingView ruhuyla, bu komut dosyasının mimarı, yatırımcıların işlevselliğini inceleyip doğrulayabilmesi için onu açık kaynaklı hale getirdi. Yazarı tebrik ederiz! Ücretsiz olarak kullanabilseniz de, kodu yeniden yayınlamanın Topluluk Kurallarımıza tabi olduğunu unutmayın.
Get exclusive indicators & AI trading strategies: luxalgo.com
Free 150k+ community: discord.gg/lux
All content provided by LuxAlgo is for informational & educational purposes only. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Free 150k+ community: discord.gg/lux
All content provided by LuxAlgo is for informational & educational purposes only. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Feragatname
Bilgiler ve yayınlar, TradingView tarafından sağlanan veya onaylanan finansal, yatırım, alım satım veya diğer türden tavsiye veya öneriler anlamına gelmez ve teşkil etmez. Kullanım Koşulları bölümünde daha fazlasını okuyun.
Açık kaynak kodlu komut dosyası
Gerçek TradingView ruhuyla, bu komut dosyasının mimarı, yatırımcıların işlevselliğini inceleyip doğrulayabilmesi için onu açık kaynaklı hale getirdi. Yazarı tebrik ederiz! Ücretsiz olarak kullanabilseniz de, kodu yeniden yayınlamanın Topluluk Kurallarımıza tabi olduğunu unutmayın.
Get exclusive indicators & AI trading strategies: luxalgo.com
Free 150k+ community: discord.gg/lux
All content provided by LuxAlgo is for informational & educational purposes only. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Free 150k+ community: discord.gg/lux
All content provided by LuxAlgo is for informational & educational purposes only. Past performance does not guarantee future results.
Feragatname
Bilgiler ve yayınlar, TradingView tarafından sağlanan veya onaylanan finansal, yatırım, alım satım veya diğer türden tavsiye veya öneriler anlamına gelmez ve teşkil etmez. Kullanım Koşulları bölümünde daha fazlasını okuyun.